BTOES From Home - SPEAKER ...
Courtesy of Nintex Pty's Paul Hsu, below is a transcript of his speaking session on 'Improve employee productivity during and post-COVID by ...
View our schedule of industry leading free to attend virtual conferences.
Each a premier gathering of industry thought leaders and experts sharing key solutions to current challenges.
Watch On-Demand Recording - Access all sessions from progressive thought leaders free of charge
from our industry leading virtual conferences.
The premier Business Transformation & Operational Excellence Conference. Watch sessions on-demand for free.
Use code: BFH1120
Delivered by the industry's most progressive thought leaders from the world's top brands.
Start learning today!
Whilst there is no single definition of Lean Methodology, there are a number of key tools, concepts and principles that can round out our view of Lean process, production and thinking.

Image courtesy of the Lean Accountants
Lean includes a wide range of principles and tools with the goal of identifying and removing waste to increase process velocity. Put in plainer terms, Lean practises seek to maximise value to the customer or client, whilst minimizing waste of all kinds.

A Lean organization, theoretically, should have the following characteristics:
With this in mind, a perfect Lean organization would have zero waste, and perfect value creation.
Key Links:
The 7 wastes, in Lean, are considered to be the root of all unprofitable activity within an organization.
The easiest way to describe waste in the context of Lean methodology is as “Something that does not add Value.” Customers would not be happy to pay for any action taken that does not add value to what they actually want.
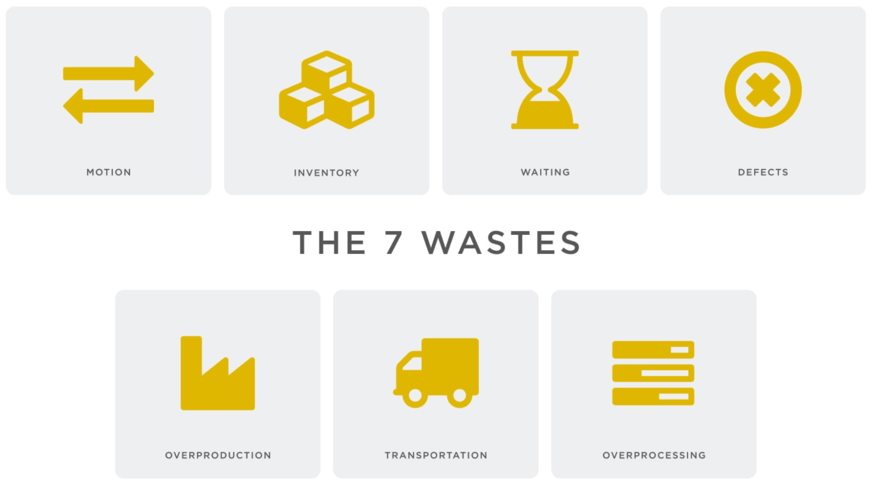
The 7 wastes consist of:
1. Defects
Defects are the most obvious of the seven wastes, although not always the easiest to detect before they reach your customers. Any mistakes made in production, or with the products themselves, come at great cost.
2. Overproduction
Overproduction leads to high levels of inventory, which can mask many of the problems within your organization. In lean methodology, batch processing, creating more supply than demand, etc. are two of the more deadly forms that overproduction can take.
3. Transportation
Transport is the movement of materials from one location to another - this is a waste as it adds zero value to the product.
4. Waiting
We tend to spend an enormous amount of time waiting for things in our working lives. Time wasted waiting on an engineer, or member of the team, often through more bureacratic processes, is a particularly dangerous and pervasive form of waste, that can take a long time to remedy or minimize.
5. Inventory
Inventory costs money - every piece of product tied up in raw material, work in progress or finished goods has a cost and until it is actually sold, that cost is yours.
6. Motion
The waste of 'motion' is best explained as unnecessary movement of any kind - a machine that takes more effort than needed to operate, workstations being far apart that require movement between, etc.7. Processing
In lean; small is beautiful - the use of small appropriate machines where they are needed in the flow is far more beneficial than massive machinery that can stop an entire process for days on end.
Though often conflated to the more dominant methodology of Lean Six Sigma, Lean does have a number of key differences to the Six Sigma methodology.
Six Sigma and Lean methodologies do have essentially the same goal. They both seek to eliminate waste, creating the most efficient system possible. However, they take different approaches with how to go about achieving this goal. In simplest terms, the main difference between Lean and Six Sigma is that they identify the root cause of waste , or 'Muda', differently.
Lean practitioners believe that waste comes from unnecessary steps in the production process that do not add value to the finished product, while Six Sigma proponents assert that waste results from variation within the process.
Lean relies on a number of key tenents, tools and principles following the Japanese method of 'Kaizen' (or 'change for the better'). Below are a few of the most critical Lean tools, employed to transform companies & manufacturers into Operational Excellence practitioners.
In the world of Lean Manufacturing, takt time is the rate at which the finished product needs to be completed, in order to meet the customer demand. Outside of Lean, the term references the german word for a Baton used to keep a tempo, or a 'heartbeat'.
The Takt Formula
Takt = T/D
Where T is Time available to create the product/service.
D is a demand for the number of units
T gives information on production pace or units per hours.
Example
An example of Takt Time would be as follows:
A company has a demand for 400 units a day, and operates for 800 minutes = 800 minutes / 400 units = a Takt Time of 2 minutes per unit.
Learn more about Takt Time now
The 5S methodology is a helpful Lean Manufacturing tool as it offers the straightforward 5-step process to ensuring the work area is organized and running efficiently - i.e. there is no wasted time whilst workers search for items/papers. The 5 s's are:
Read the full Lean 5S guide now
The antithesis to 'batch' production, continuous flow manufacturing is the process of keeping a product moving from the beginning of production to the completion of the product. It is used in manufacturing to maximise efficiency against 'batching', as the next product can be introduced to the process as soon as the one before has completed step one.

Gemba is a philosophy in Lean Manufacturing that expresses the principle of going to the shop floor. It reminds leadership within a company practising Lean to visit the plant floor, and gain understanding of the 'real action'. Going to Gemba provides leadership with an understanding of the real processes and day-to-day undertaking of Lean principles.
'Taking your Operational Excellence Program to the Next Level' focuses on 3 key takeaways:
About this Video Presentation:
Key Learning Takeaways include:
Further Reading
Welcome to BTOES Insights, the content portal for Business Transformation & Operational Excellence opinions, reports & news.
Insights from the most progressive thought leaders delivered to your inbox.
Insights from the world's foremost thought leaders delivered to your inbox.
Being a hero is all about creating value for others. Please invite up to 5 people in your network to attend this premier virtual conference, and they will receive an invitation to attend.
If it’s easier for you, please enter your email address below, and click the button, and we will send you the invitation email that you can forward to relevant people in your network.
View our schedule of industry leading free to attend virtual conferences. Each a premier gathering of industry thought leaders and experts sharing key solutions to current challenges.
View Schedule of EventsWatch On-Demand Recording - Access all sessions from progressive thought leaders free of charge from our industry leading virtual conferences.
Watch On-Demand Recordings For FreeDelivered by the industry's most progressive thought leaders from the world's top brands. Start learning today!
View All Courses NowThe premier Business Transformation & Operational Excellence Conference. Watch sessions on-demand for free. Use code: BFH1120
Watch On-DemandInsights from the most progressive thought leaders delivered to your inbox.
Insights from the world's foremost thought leaders delivered to your inbox.
Being a hero is all about creating value for others. Please invite up to 5 people in your network to also access our newsletter. They will receive an invitation and an option to subscribe.
If it’s easier for you, please enter your email address below, and click the button, and we will send you the invitation email that you can forward to relevant people in your network.
Courtesy of Nintex Pty's Paul Hsu, below is a transcript of his speaking session on 'Improve employee productivity during and post-COVID by ...
Read this article about HP, Best Achievement in Operational Excellence to deliver Digital Transformation, selected by the independent judging panel, ...
Read this article about BMO Financial Group, one of our finalists, in the category Best Achievement in Operational Excellence to deliver Digital ...
Read this article about Cisco, one of our finalists, in the category Best Achievement of Operational Excellence in Internet, Education, Media & ...